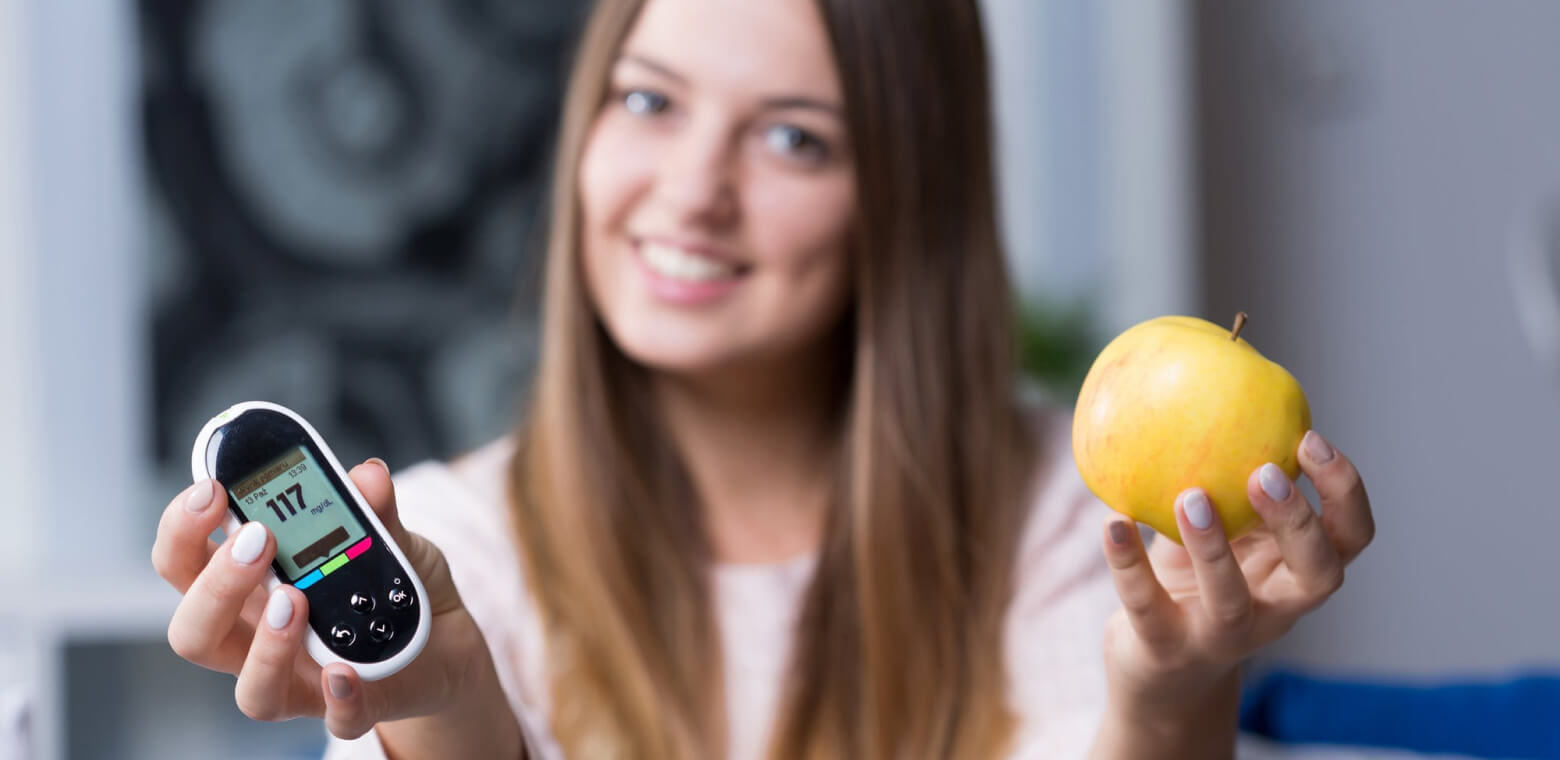
According to the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, in 2021, 2,000,325 people suffering from diabetes were recorded in Ukraine. In 2017, this number was half as much - 1 270 929 people. Statistics only take into account those who seek medication, but many people do not even know that they are at risk and need treatment.
What is diabetes and what it looks like
According to the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, in 2021, 2,000,325 people with diabetes were recorded in Ukraine. In 2017, this number was half as much - 1 270 929 people. Statistics only take into account those who seek medication, but many people do not even know that they are at risk and need treatment.
According to the World Health Organization, 50% of patients die from cardiovascular failure, 10% suffer from severe visual impairment, 2% - complete blindness, 10% to 20% - suffer from kidney failure. Also among the most common consequences of diabetes are: diabetic foot syndrome, development of neuropathy, micro- and macroangiopathy.
In medical practice, there are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes This type of disease is called insulin-dependent because the body cannot produce insulin on its own, and the patient needs a daily dose of medication to prolong life. Type 1 diabetes is most common in children and adolescents. But in medical practice, there have been growing numbers of isolated cases when the disease occurred in adults under 30 years of age. Approximately 10% of those patients who consulted a doctor with characteristic symptoms suffer from type 1 diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes About 90% of patients are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. It is also called insulin-independent, because the hormone is produced in the body, but blood cells do not react to it. Insulin injections as a treatment are used only in extreme cases. With timely diagnosis of the disease, it is possible to effectively influence the patient's condition by changing lifestyle and adjusting the diet. Most often, type 2 diabetes is diagnosed in women over 30 years old.

Symptoms of diabetes
In the initial stages, type 1 and type 2 diabetes manifests itself almost identically. In both cases, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- severe hunger and constant thirst;
- frequent and excessive urination;
- sleep disturbances and increased fatigue;
- a veil in front of the eyes;
- rapid weight gain or loss;
- slow healing of wounds;
- dry and rough skin;
- itching;
- swelling.
If you have three or more of these symptoms, you need to test your blood glucose level. If the test results show its concentration is more than 6.5 mm/l on an empty stomach or more than 12 mm/l immediately after eating, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Why the disease occurs
It is still not known exactly why the pancreas stops producing insulin, and no prevention measures have been developed. In 50% of cases, type 1 diabetes is inherited, in the rest - it appears after infections and viruses. Scientists around the world continue to investigate the causes of the disease, its course and methods of prevention, but certain patterns have already been identified.
In medical practice, there are several main causes of diabetes:- Heredity People whose parents have been diagnosed with the disease are at risk. From an early age, they should follow a healthy lifestyle and monitor their diet.
- Endocrine diseases Diabetes, in particular type 2, can develop as a result of thyroid dysfunction, with a tumor of the pancreas.
- Infectious diseases In people with a hereditary predisposition to diabetes, its first symptoms are often detected after viruses, against the background of inflammatory processes.
- Obesity A large amount of adipose tissue negatively affects the susceptibility of cells to insulin entering the blood. 80% of patients with the diagnosed disease are overweight.
- Improper nutrition A large amount of sugar in the diet leads to insulin surges, which contributes to the development of the disease. Overeating is the main cause of obesity.
- Physical inactivity A sedentary lifestyle slows down metabolic processes in the body. Muscles consume less glucose, and it accumulates in the blood.
How the disease develops
Type 1 diabetes begins when the immune system attacks the cells of the pancreas and permanently destroys their ability to produce insulin. When the body produces enough insulin, glucose from the blood enters the cells of various organs, and its remains are stored in the liver and muscle tissues. If a person needs additional energy between meals, for example, during sleep or exercise, the body uses these residues.
In type 1 diabetes, due to the lack of insulin, glucose does not enter the cells, its level increases rapidly, so the signs of the disease appear quickly enough. Patients immediately feel very thirsty and dry mouth, wake up several times at night to go to the toilet, and their urine volume increases significantly.
In type 2 diabetes, body tissues gradually consume and utilize less and less glucose. Blood sugar levels can rise for years and not cause any symptoms of the disease. Over time, the body begins to excrete excess glucose through the kidneys. Together with urine, salts and fluids are excreted from the body, which causes dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Then the first symptoms of the disease appear.
If diabetes is left untreated, high sugar levels cause problems in all key systems of the body:- Heart and blood vessels Fatty deposits on the walls of blood vessels cause poor blood circulation, leading to hypertension, atherosclerosis, strokes and heart attacks.
- Kidneys Due to the increased load, they gradually stop filtering blood - kidney failure develops.
- Eyes Due to damage of small vessels, swelling of the lens occurs and vision deteriorates, the risk of cataracts, glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy increases.
- Nervous system Hands and feet become numb, there are problems with digestion and genitourinary system, libido decreases.
- Skin Wounds and scratches heal poorly and for a long time, the risk of fungal and bacterial diseases increases.
In advanced cases of diabetes, feet suffer, which in most cases cannot be saved and have to be amputated.


Modern methods of treatment
Diabetes treatment is a way of life. The following methods are used to keep the disease under control:
-
Insulin therapy
People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day, the required amount of which can vary throughout the day. Therefore, patients regularly check their blood glucose levels to find out what dose of medication is needed right now. Diet and exercise can affect sugar levels.
Insulin in type 2 diabetes is used in several cases: if the disease has become severe, in surgical and emergency conditions, during pregnancy. The indication for the appointment of insulin injections is often the ineffectiveness of drugs in tablets. - Measurement of blood sugar Regular monitoring of glucose levels can increase the effectiveness of treatment and prevent the development of the disease. Measurements are carried out by the patient several times a day. The doctor sets the norm of indicators for each patient individually.
- POCTech continuous blood glucose monitoring systems The device is small in size, so it is convenient to place on the patient's abdomen or arm. All data from it is transferred to a smartphone and updated in real time.
- Insulin pumps A small device in the body of which there is a tank with insulin. The pump transports insulin into the body continuously, according to the regimen programmed by the doctor.
- Curasonix This system was developed to solve problems with the complexity of wound healing. It gently and effectively cleanses the wound through three mechanisms of action: macroabrasion, microabrasion and ultrasound. The use of the Curasonix system can significantly reduce the risk of infection and the number of cases of limb amputation.
- Diet and exercise In diabetes, the amount of rapidly digestible carbohydrates in the patient's diet is severely limited, as their use provokes blood sugar spikes and promotes weight gain. Physical exercises help to speed up metabolism and reduce body weight, if necessary. You can find many different diets for diabetes on the Internet, but a doctor should prescribe medical nutrition. The specialist selects the diet and the level of stress after studying the patient's tests.
- Medicines that lower sugar Antidiabetic pills help regulate the activity of insulin and the susceptibility of body tissues to it. They are prescribed to people to maintain the correct blood sugar level. Medications are always used in combination with diet and physical activity, prescribed by an endocrinologist.
Prevention of diabetes
In most cases, diabetes can be prevented. To do this, you need to:
- Adhere to the rules of healthy eating.
- Be physically active.
- Maintain a normal body weight.
- Monitor the metabolism.
- Give up smoking and alcohol.
The danger of the disease is that in the early stages it does not manifest itself in any way, so you need to take an annual blood sugar test on an empty stomach. At the slightest irregularities in the tests, the doctor will refer you for a full examination to find out the causes of high blood glucose concentration and prescribe further treatment. Blood sugar test can be done free of charge with a referral from a family doctor.
How to successfully live with diabetes?
The main factor of success in controlling diabetes is strict adherence to all doctor's recommendations. First of all, you need to change your lifestyle:
- Switch to a medical diet Doctors note that it is necessary to exclude from the diet sugar, corn, potatoes, grapes, figs, dates, raisins, strawberries and bananas, white rice, muesli and cereals, fatty dairy products, bakery products made of puff and pastry dough, because they quickly increase blood glucose levels. If you really want to eat something tasty, it is better to give preference to sweets for diabetics. It is very important for patients with diabetes to eat according to the regimen and consume the calorie intake prescribed by a nutritionist.
- Adding physical activity With sports such as yoga, tennis, swimming, dancing, football and Pilates helps to keep sugar levels in check. However, you need to coordinate the chosen physical activity with your doctor and do not train if you feel unwell. It is better to limit the training time to one hour a day and warn the trainer about your health condition. It is also necessary to measure sugar levels before and after training to protect yourself.
- Lose weight and give up bad habits Alcoholic drinks contain a lot of sugar and increase its level in the blood. Smoking negatively affects the state of the whole body, and especially the cardiovascular system. And excess weight adds to the burden on the heart and other organs. The healthier the patient's body, the lower the risk of disease-related complications.
- Take medications in prescribed doses Insulin injections are necessary to maintain normal blood glucose levels. A drop in sugar to critically low levels can cause weakness and dizziness, and in severe cases - loss of consciousness, seizures and coma.
Diabetes requires constant attention and monitoring of the body: measuring blood sugar, blood pressure, metabolic processes. Regular examinations and timely correction of treatment can prevent the development of the disease and lead a normal life of a healthy person.








